
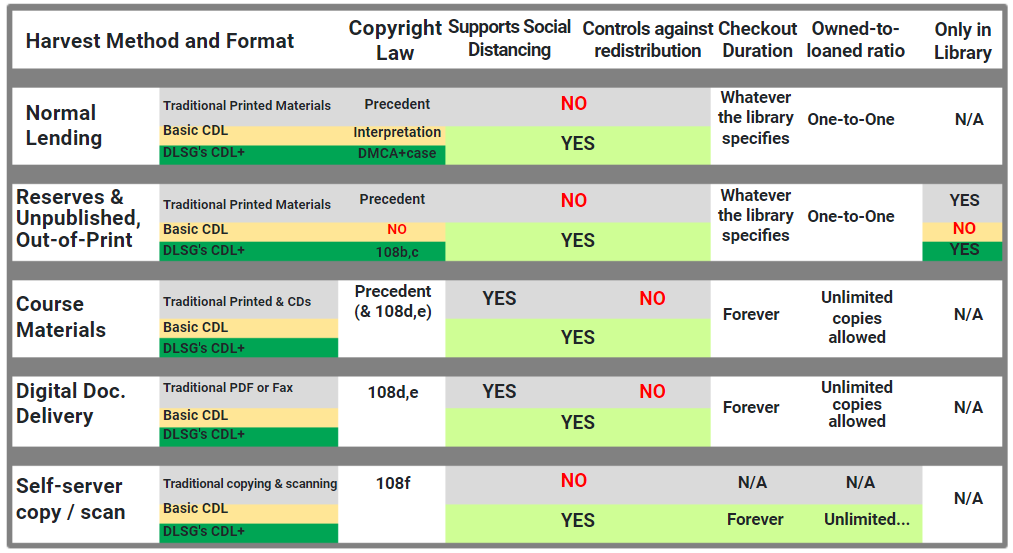
The U.S. Patent Office’s Section 108 Study Group has been working for 20 years and has not come to an agreement. Perhaps it’s time for a new approach. DLSG’s answer, Aggregate CDL serves copyrights holders and libraries, but most of all, citizens at large.
The U.S. Constitution allows copyright law to exist for the sole purpose of promoting the authoring and publishing of works that benefit society. And while many scholarly monographs are created to fill the “publish or perish” directive, scholarly monographs are important and sometimes essential facilitators of the development of new science and technology, and to improve the human condition. However, over the past 20 years, monograph publishing rates have declined significantly.
DLSG’s Aggregate CDL is designed to expose researchers and students to vastly more relevant content from scholarly monographs while in the library. And when not in the library, the user is given the opportunity to rent or buy the content, presumably using department or personal funds This provides the revenue impetus authors and publishers need to write and publish more monographs, without using library funds. And once Aggregate CDL is setup, the ‘in the library’ requirement can be relaxed from the first day of the next pandemic, and ended when the institution deems appropriate.
DLSG’s Aggregate CDL system includes HotLinks Research Tool, which allows the user to input entire research papers for the system to characterize and perform DLSG’s exclusive search and match function and provide instant access to 100 of the most relevant items from your library, and highlight important content. When the user leaves the library, the content is not accessible, but the highlights are retained, up to 10% of the content of each volume reviewed. The user can access the content while not in the library, if desired, by simply renting or buying the desired content. Upon returning to the library, the content is again visible, with the highlights. The highlights can also be output in an editable format with source citations
In summary, DLSG’s Aggregate CDL:
- Provides a revolutionary new method of discovery and analysis designed specifically for researchers and students, a method that instantly exposes them to large numbers of relevant print collections items
- Provides full access to all content of all copyrighted items in the library’s print collections, while in the library
- Strongly promotes the library as an extremely effective research center
- Promotes the purchase or rental of copyrighted content when not in the library for those who can afford it, and as a consequence, promotes the authoring and publishing of more scholarly monographs, not just for credentialing the author, but to advance science, technology and the human condition.
1-to-1 Lending – students must wait
1-to-Many Lending – no waiting
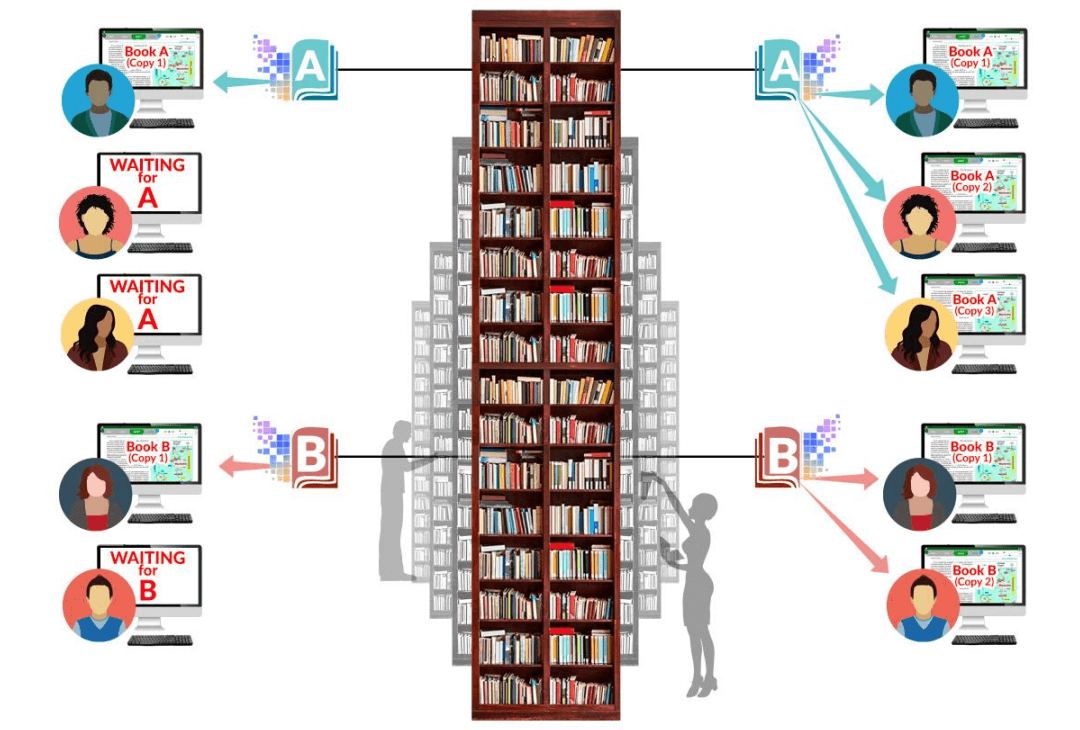
Basic CDL has a simple one-to-one owned-to-loaned ratio requirement. If the library owns only one printed copy of book A and one printed copy of book B, it can simultaneously lend only one digital copy of book A and one digital copy of book B. Basic CDL does not allow a library to lend multiple digital copies when it owns only one printed copy of a book.
Aggregate CDL also has an owned-to-loaned ratio requirement, but that requirements is based on dollars spent and lent. If in a given year, a library buys only one printed copy of book A and one printed copy of book B from a particular publisher, but also buys a sufficient number of esoteric scholarly monographs from the same publisher, the library can lend more copies of books A and B than it owns, provided the total dollars spent is less than or equal to the total dollar value lent.
With Basic CDL, to avoid waiting, the library must buy multiple copies of common books
With Aggregate CDL, spending and publisher revenue are the same, but the library gets a bonus: esoteric scholarly monographs
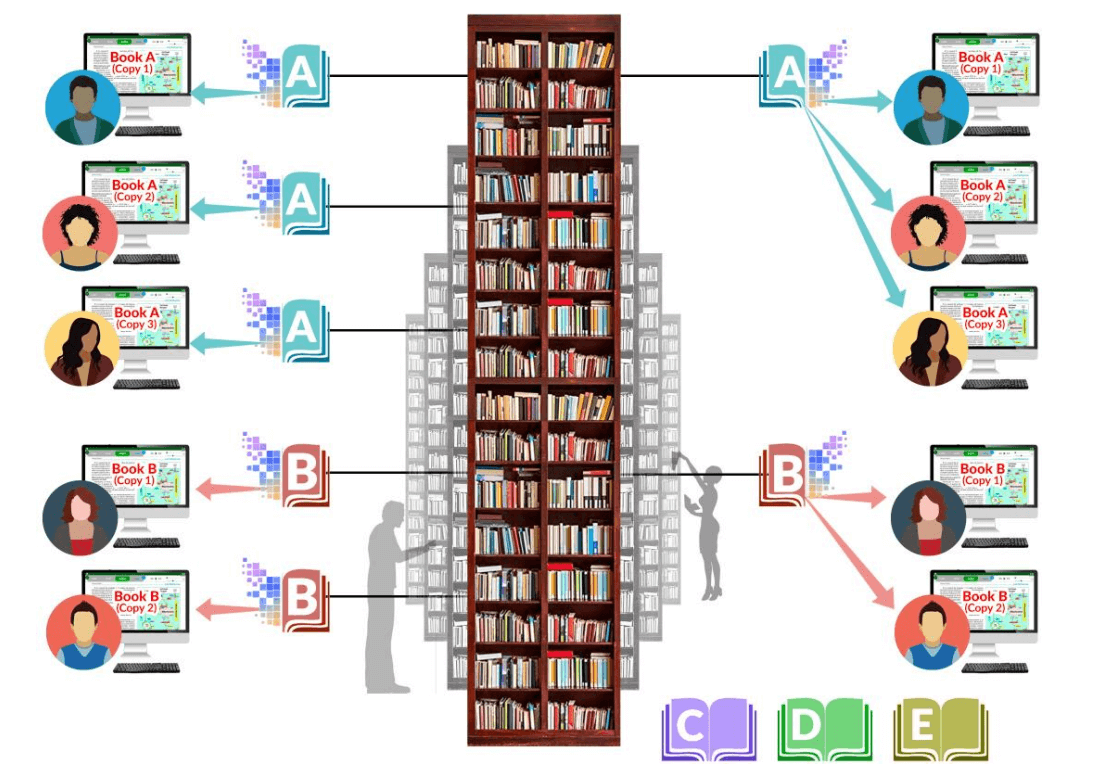
The Aggregate CDL Bonus: more esoteric scholarly monographs at no additional cost.
With basic CDL, if a library wishes to allow several students to checkout the same book simultaneously, the library must purchase multiple additional copies of that same book. This is wasteful and it does not promote the publishing of esoteric scholarly monographs.
With aggregate CDL, the library can spend the same dollar amount with a particular publisher, but buy only one copy of each popular book that it needs, and spend the balance of the money on esoteric scholarly volumes, represented above by books C, D and E in the diagram above. The rule for this example, in summary is: